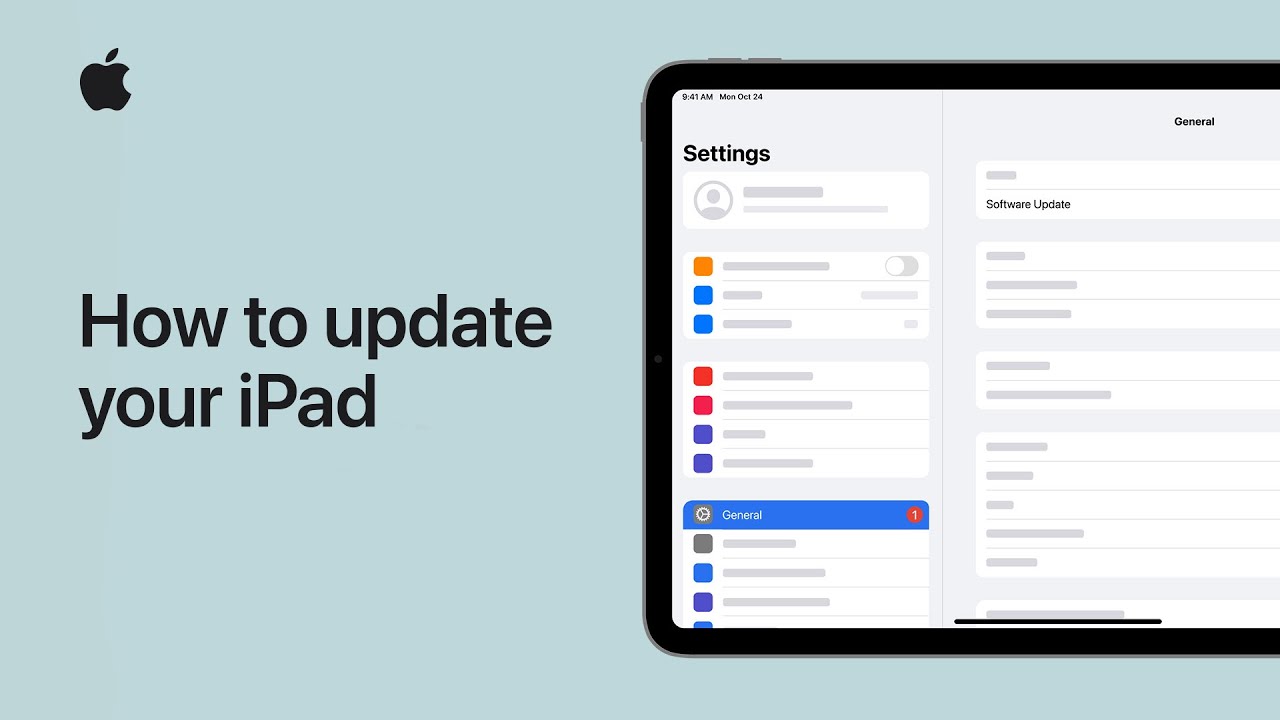
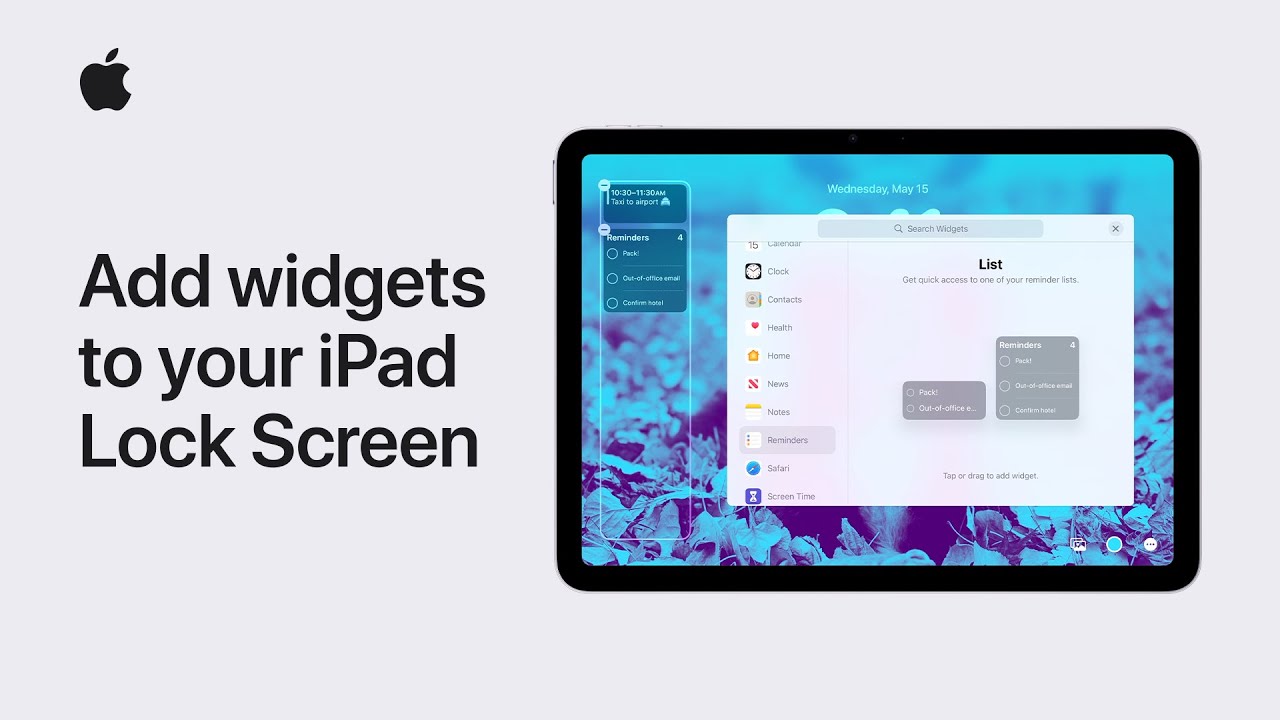
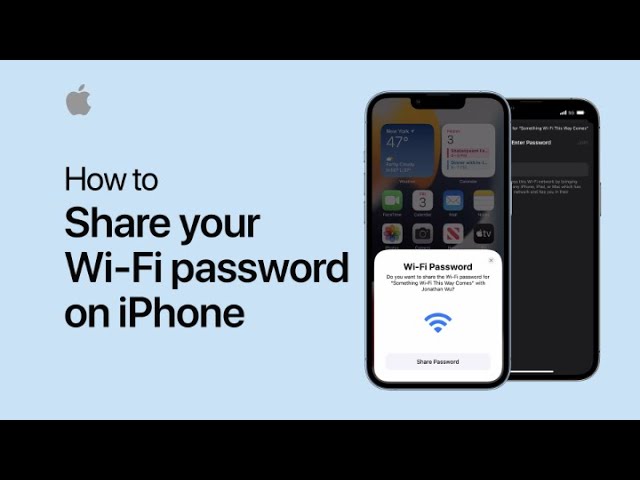
Artificial intelligence, or AI, is popping up everywhere—from online shopping and customer service to healthcare and transportation. But as AI becomes more common, many people are asking: Who’s making sure it’s safe and fair?
The answer lies with governments. Around the world, lawmakers are stepping in to create rules that guide how AI is built and used. These rules aim to protect people’s privacy, prevent misuse, and make sure AI benefits everyone—not just big tech companies.
In this easy-to-follow guide, we’ll look at how different countries are handling AI regulation. Whether you’re just curious or trying to understand what this means for your daily life, we’ll walk you through it in a way that’s simple and clear.
Table of Contents
Key Takeaways
- AI is growing quickly, and countries are rushing to set guidelines.
- Europe leads with the strongest rules, focusing on safety, transparency, and human rights.
- The U.S. takes a flexible approach, relying more on industry guidance than strict laws.
- China uses AI to support national goals, with heavy government oversight.
- Many other countries are developing their own strategies, often inspired by global trends.
- International cooperation is starting, but full global rules don’t exist yet.
How Countries Are Approaching AI Regulation
Let’s break it down country by country.
European Union (EU): Leading the Way with the AI Act
The EU is often seen as the strictest when it comes to regulating technology. In 2024, it passed the AI Act, the world’s first major law focused only on AI.
Key Features:
- AI systems are ranked by risk: low, limited, high, and banned.
- High-risk AI (like facial recognition in public) must meet strict rules.
- Transparency is required—people should know when they’re interacting with AI.
- The focus is on protecting human rights, fairness, and safety.
This approach aims to make sure AI doesn’t harm people or their freedoms. It also encourages companies to build trustworthy technology.
United States: Industry-Led, Flexible Policies
The U.S. has not passed a nationwide AI law yet. Instead, it follows a lighter, more flexible path. Agencies like the Federal Trade Commission (FTC) and the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) are offering guidance, not strict rules.
Key Features:
- Guidelines encourage companies to be ethical and transparent.
- AI regulation is often handled by individual states or sectors (like healthcare or finance).
- President Biden signed an Executive Order in 2023 calling for safe and secure AI development.
The U.S. approach aims to avoid slowing down innovation but may fall short in protecting the public without stronger rules.
China: Strong Government Control and Strategy
China uses AI in many areas, including security, manufacturing, and online services. The government sees AI as key to national growth, so it takes a highly controlled approach.
Key Features:
- Strict rules govern AI-generated content, like deepfakes or chatbots.
- Companies must register some AI systems with the government.
- AI is used for surveillance and social scoring in some areas.
China’s model focuses on control and national benefit. It raises concerns about privacy and freedom but reflects a very different approach to managing technology.
Canada, Japan, and Other Nations: Finding a Middle Ground
Many other countries are developing their own AI strategies:
Canada
- Created the Directive on Automated Decision-Making for government use of AI.
- Focuses on accountability and transparency in public services.
Japan
- Supports innovation while encouraging ethical use.
- Works closely with businesses to create practical guidelines.
United Kingdom
- Plans to regulate AI based on how it’s used rather than one-size-fits-all laws.
- Encourages flexible rules that match different sectors.
These countries often draw inspiration from both U.S. flexibility and EU protections, aiming for a balanced approach.
Global Cooperation: A Work in Progress
Because AI is used across borders, many leaders believe we need global rules. So far, cooperation is still in the early stages.
Efforts Include:
- The G7 AI Code of Conduct, which encourages responsible AI use.
- The OECD AI Principles, which many countries have agreed to follow.
- The United Nations is discussing ways to shape international AI guidelines.
These aren’t laws yet—but they show that countries are trying to work together on shared values like safety, fairness, and human dignity.
Final Thoughts
AI is a powerful tool, and governments around the world are racing to keep up with it. Whether they’re creating strict rules like the EU, flexible policies like the U.S., or national strategies like China, one thing is clear: AI is too important to leave unregulated.
For everyday people, these regulations can help protect privacy, reduce harm, and ensure AI is used for good. As policies continue to develop, staying informed can help you understand how these decisions may affect your rights, your job, or your community.
Want to learn more about how AI is shaping daily life? Check out our guides on AI in healthcare, education, and beyond.